The Body: Physical Fitness
The 5 primary components of physical fitness are flexibility, cardiovascular exercise, muscular endurance, muscular strength, and body composition. The 5 components of physical fitness combine the necessary ingredients to be in the best physical condition possible. When starting an exercise program, each individual should include these 5 components to achieve the maximum results within their exercise program.
THE F.I.T.T. PRINCIPLE
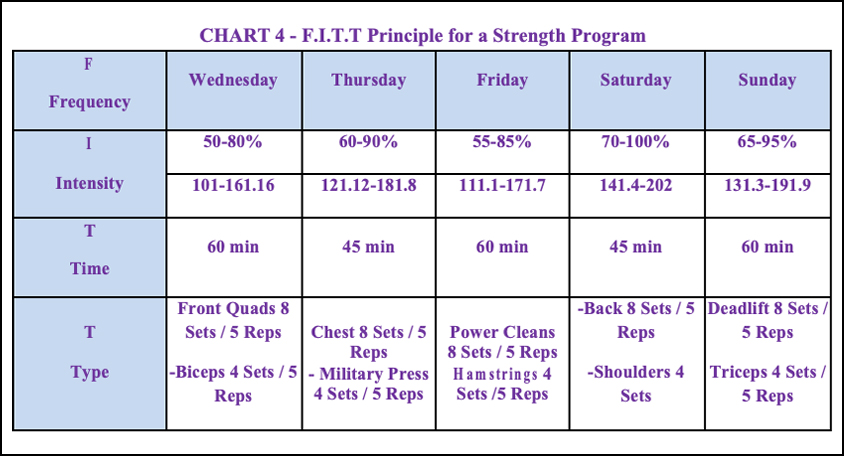
THE F.I.T.T PRINCIPLE is a formula that monitors an exercise/fitness program at all levels. The acronym FITT represents Frequency, Intensity, Time, and Type. Although the F.I.T.T. principle is commonly used in the weight loss industry, it can also be a part of strength and conditioning programs.
Frequency is defined as the how often you exercise (day, weekly, monthly, etc.)
Intensity is defined as how hard you exercise
Time is defined as refers to the time how long you exercise
Type is defined as what kind of exercise is performed
F.I.T.T. Principle Basic Recommendation for Results
Frequency – 5 to 6 times per week
Intensity – raising the heart rate rises in a training zone (beats per mins) during exercise
Time – 60-90 minutes
Type – The exercise choices used for the workout routine may include cardiovascular, muscular endurance, muscular strength, or flexibility exercises. The type can include all types at once using a circuit or cross fit routine.
Definitions
Maximum Heart Rate (MHR) = 220 – age
Target Heart Rate (THR): A heart rate that is reached during aerobic exercise that represents the minimum level of exertion at which cardiovascular fitness can increase for an individual at any given age group. THR is usually a pre-determined pulse rate to target during aerobic (ex: 60%)
Target Heart Rate Zone (THZ): An estimated range of how fast your heart should beat during exercise. It should be a safe but effective range for a specific workout.
A quick way to measure the training heart rate is by taking the pulse for 6 seconds. Add a zero to the number of beats from the pulse = 70 bpm (example: if the pulse rate is 7 for 6 seconds, add a 0 to the pulse rate but for the best and most accurate results use a heart rate monitor).
Intensity and the F.I.T.T. Principle
STEP 1 - Maximum Heart Rate (MHR): If Jane is 20 years old what is her maximum heart rate (MHR): 220 – 20 = MHR for Jane is 200.
STEP 2 - Target Heart Rate (THR): Joey is 40 years old. He has decided to put forth a 100% effort in losing his weight with a good exercise routine and a fun-filled diet (no fad diets; he is watching his glycemic index and his caloric intake). Since Joey weighs 600 pounds, Dr. Sims has started him on an exercise routine for the first 3 months that involves walking for 20-30 minutes per day 6 days per week (walk around the corner, treadmill, or at the local college or high school track). Dr. Sims gave Joey a target heart rate of 60%. To make this an easy fitness journey, Joey purchased a heart monitor for the next 3-months to assist him in tracking his target heart rate. After 3-months Joey has reduced his weight from 600 to 546 pounds. Now that Joey feels comfortable about his exercise routine, Dr. Sims has suggested that Joey use a training heart rate zone. This type of zone allows Joey to speed up his heart rate (higher beats per min = bpm) while exercising. Also, the heart rate training zone will allow Joey the freedom to slow down his heart rate (lower bpm) at any time. Using the target heart rate zone allows Joey to walk a little faster, yet slow down to catch his breath at any time.
Example Using Joey
Equation for Target Heart Rate (THR)
MHR = 220 – 40 = 180
THR = MHR x 60% (note, 60% = 0.60, Joey’s Doctor informed him to target 60%)
THR = 180 x .60 = 108 beats per minute
Equation for Target Heart Rate Zone (THZ)
THZ = MHR x two percentages to create a low and a high area (zone) for your heart rate (bpm) during the entire exercise routine
MHR = 220 – 40 = 180
1st Zone (60%):
THR = 180 x .60 = 108 beats per minute
2nd Zone (80%):
THR = 180 x .80 = 144 beats per minute
THZ = 108 and 144 beats per minute.
Along with understanding the glycemic index and calorie counting, the target heart rate zone is the healthiest way to shed pounds quickly.
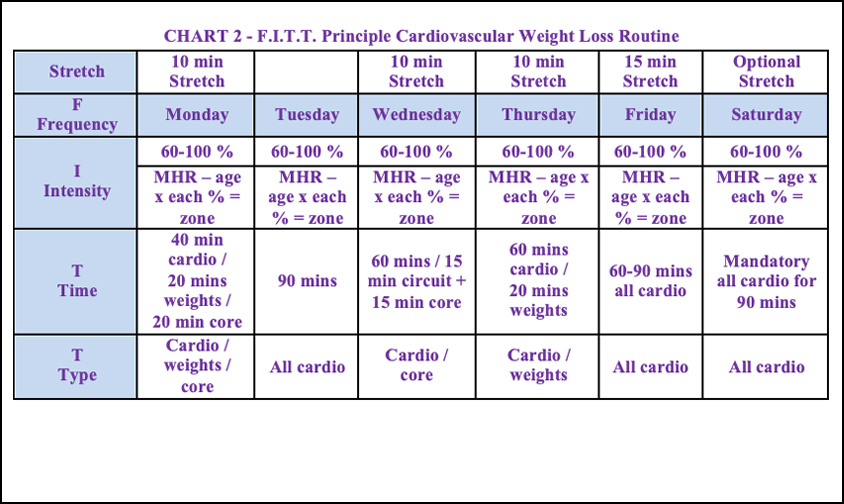
F.I.T.T. Principle for Cardiovascular
The purpose of the cardiovascular program is to promote weight loss and body tone by keeping the heart rate training zone between 60% and 100%, 6-days per week in conjunction with a good nutrition plan. Use variety when selecting cardiovascular exercises.